Will Settimeout Run Again on Page Load

Accept you ever wondered if in that location is a method to filibuster your JavaScript lawmaking past a few seconds?
In this article, I will explain what the setTimeout() method is with code examples and how it differs from setInterval().
What is setTimeout() in JavaScript?
setTimeout() is a method that will execute a slice of code afterward the timer has finished running.
Here is the syntax for the setTimeout() method.
let timeoutID = setTimeout(office, filibuster in milliseconds, argument1, argument2,...); Let's break down the syntax.
Part
setTimeout() will set a timer and in one case the timer runs out, the function will run.
Filibuster in milliseconds
Inside this method, you lot can specify how many milliseconds you want the role to filibuster. 1,000 milliseconds equals one second.
In this example, the bulletin will announced on the screen after a delay of iii seconds. (3,000 milliseconds)
const para = document.getElementById("para"); role myMessage() { para.innerHTML = "I just appeared"; panel.log("message appeared"); } setTimeout(myMessage, 3000); If the filibuster is not present in the setTimeout() method and then it is set to aught and the bulletin will announced immediately.
const para = certificate.getElementById("para"); function myMessage() { para.innerHTML = "No delay in this message"; console.log("message appeared immediately"); } setTimeout(myMessage); Arguments
You can also have optional arguments that are passed into the office.
In this example conversation, Britney will ask a question and Ashley's response will exist delayed by 3 seconds. It will include the 2 optional arguments from the lunchMenu office.
const ashley = certificate.getElementById("ashley"); function lunchMenu(food1, food2) { ashley.innerHTML = `<strong>Ashley: </strong>I had ${food1} and ${food2}.`; } setTimeout(lunchMenu, 3000, "pizza", "salad"); timeoutID
setTimeout() will return the timeoutID which is a positive integer and unique ID for the timer.
clearTimeout()
This method is used to cancel a setTimeout(). Inside the method you have to reference the timeoutID.
Here is the basic syntax.
clearTimeout(timeoutID) In this example, the message will appear after a ten 2nd (ten,000 millisecond) delay. But if the user clicks on the Stop Timer button, and so the setTimeout() will be cancelled.
const timerMsg = document.getElementById("message1"); const stopBtn = document.getElementById("finish"); function timerMessage() { timerMsg.innerHTML = "Thanks for waiting!"; } let timeoutID = setTimeout(timerMessage, 10000); stopBtn.addEventListener("click", () => { clearTimeout(timeoutID); timerMsg.innerHTML = "Timer was stopped"; }); Should yous pass in a string instead of a function for setTimeout()?
It is considered bad practice and a security take a chance to pass in a string instead of a function.
Avert writing setTimeout() similar this:
setTimeout("console.log('Practice not do this');", chiliad); Some code editors volition warn you lot and suggest using a office instead.
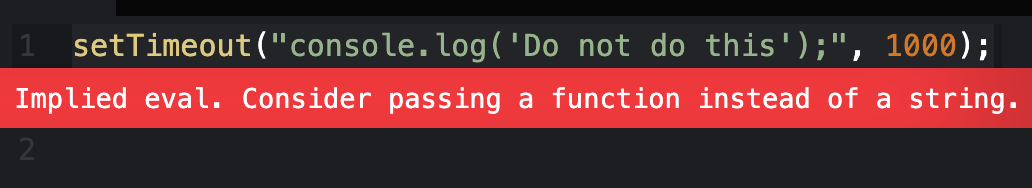
Always use a function instead of a cord in this example.
setTimeout(role () { console.log("Practice this instead"); }, 1000); If y'all want to larn more about the security risks for an implied eval, delight read about it in the MDN docs section on Never Utilise Eval.
How does setInterval() differ from setTimeout()?
Unlike setTimeout() which executes a function only once later a delay, setInterval() will repeat a function every fix number of seconds. If you want to stop setInterval(), and then y'all use clearInterval().
The syntax for setInterval() is the aforementioned every bit setTimeout().
permit intervalID = setInterval(office, filibuster in milliseconds, argument1, argument2,...); In this example, we have a sales message that is being printed to the screen every second.
allow intervalID = setInterval(() => { salesMsg.innerHTML += "<p>Sale ends soon. BUY At present!</p>"; }, g); Inside the setTimeout() method, nosotros utilize clearInterval() to stop press the bulletin after 10 seconds.
setTimeout(() => { clearInterval(intervalID); }, 10000); Just like with setTimeout(), y'all take to utilize the unique ID for the timer inside the clearInterval() method.
Real Project Examples
Now that we understand how setTimeout() and setInterval() work, let's take a expect at an case of how it tin can apply to a existent feature on a website.
In this example, we have a progress bar that will starting time 2 seconds subsequently the page loads. Inside the setTimeout(), nosotros have a setInterval() that will execute the animate() function as long equally the bar width is not 100%.
setTimeout(() => { allow intervalID = setInterval(() => { if (barWidth === 100) { clearInterval(intervalID); } else { animate(); } }, 100);//this sets the speed of the blitheness }, 2000); Inside the animate() part, we take another setTimeout() that will display 100% Completed when the progress bar is full.
const breathing = () => { barWidth++; progressBar.style.width = `${barWidth}%`; setTimeout(() => { loadingMsg.innerHTML = `${barWidth}% Completed`; }, 10100); }; A progress bar is just one of many animations you can create with setTimeout() and setInterval(). You tin also utilise these methods when building online games.
In Beau Carnes' How to Build A Simon Game you can see how setTimeout() and setInterval() are used in the game logic.
Decision
setTimeout() is a method that will execute a piece of code after the timer has finished running.
let timeoutID = setTimeout(part, delay in milliseconds, argument1, argument2,...); The delay is set in milliseconds and ane,000 milliseconds equals 1 2nd.
If the delay is omitted from the setTimeout() method, then the delay is set to 0 and the function will execute.
You tin also take optional arguments that are passed into the function.
setTimeout() will return the timeoutID which is a positive integer and unique ID for the timer.
Information technology is important not to utilise a string in place of the function for security reasons.
setTimeout("panel.log('Practice not do this');", m); If you want to cancel setTimeout() then you lot need to use clearTimeout()
clearTimeout(timeoutID) If you want to repeatedly execute a slice of code for a set amount of seconds and so y'all would utilize setInterval().
permit intervalID = setInterval(() => { // this code runs every 2nd }, 1000); setTimeout() tin can be used in building basic JavaScript animations and online games.
I hope y'all enjoyed this article on setTimeout().
Acquire to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Go started
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/javascript-settimeout-js-timer-to-delay-n-seconds/
0 Response to "Will Settimeout Run Again on Page Load"
Enregistrer un commentaire